Back in May during Bike to Work Week, MDOT and MTA announced that starting on June 1, all MARC trains would accommodate full sized bikes. This means that now the Camden, Penn, and Brunswick lines all have bike parking spots. This is huge news in improving accessibility for regional, multi-modal transit. Previously, only certain trains accommodated bikes and this was only consistent on weekend Penn Line service.
After the announcement, a number of folks have expressed concern about bike parking on the MARC trains taking away ADA spots on some cars. We reached out to the MTA for clarification on this issue and have some follow up details.
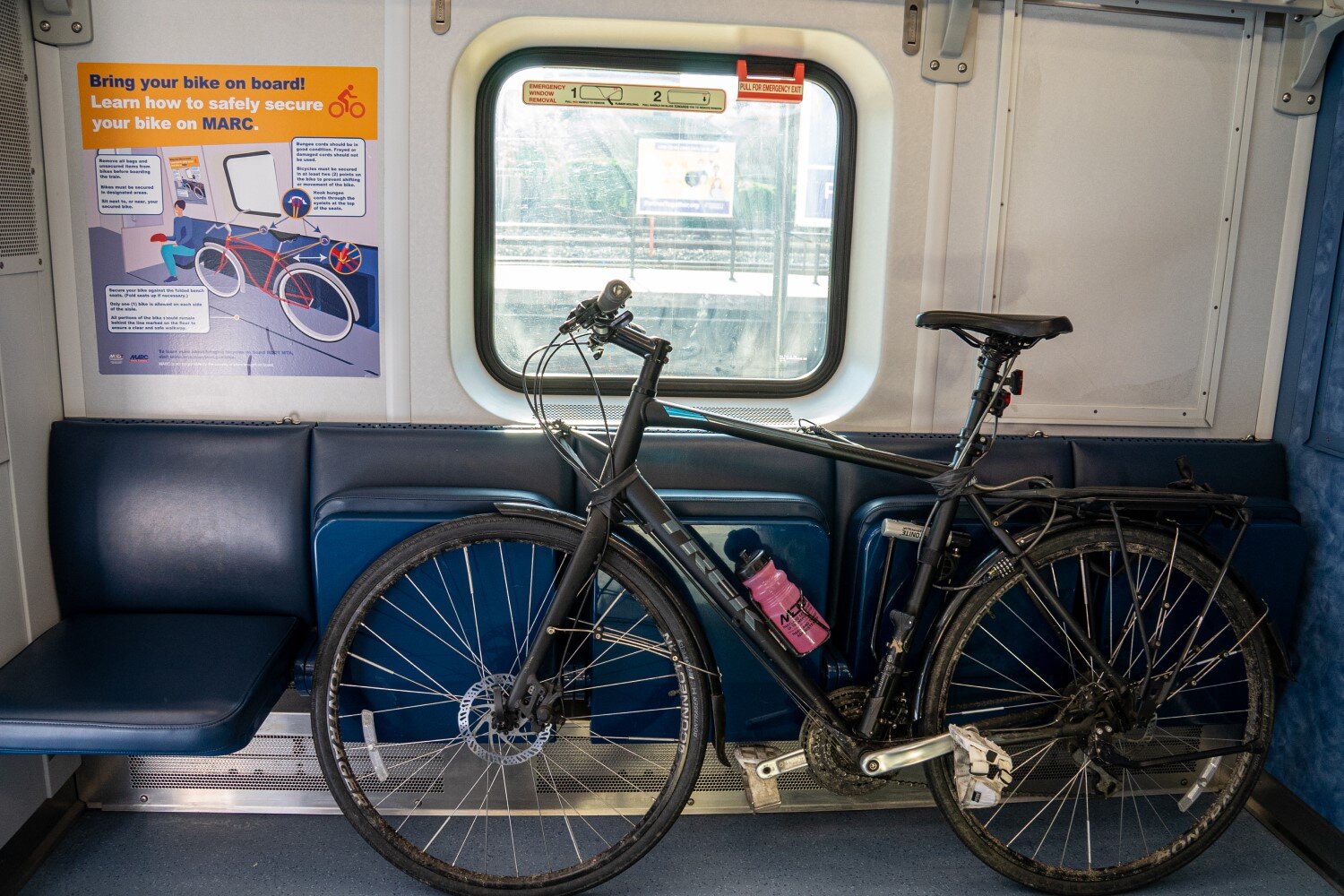
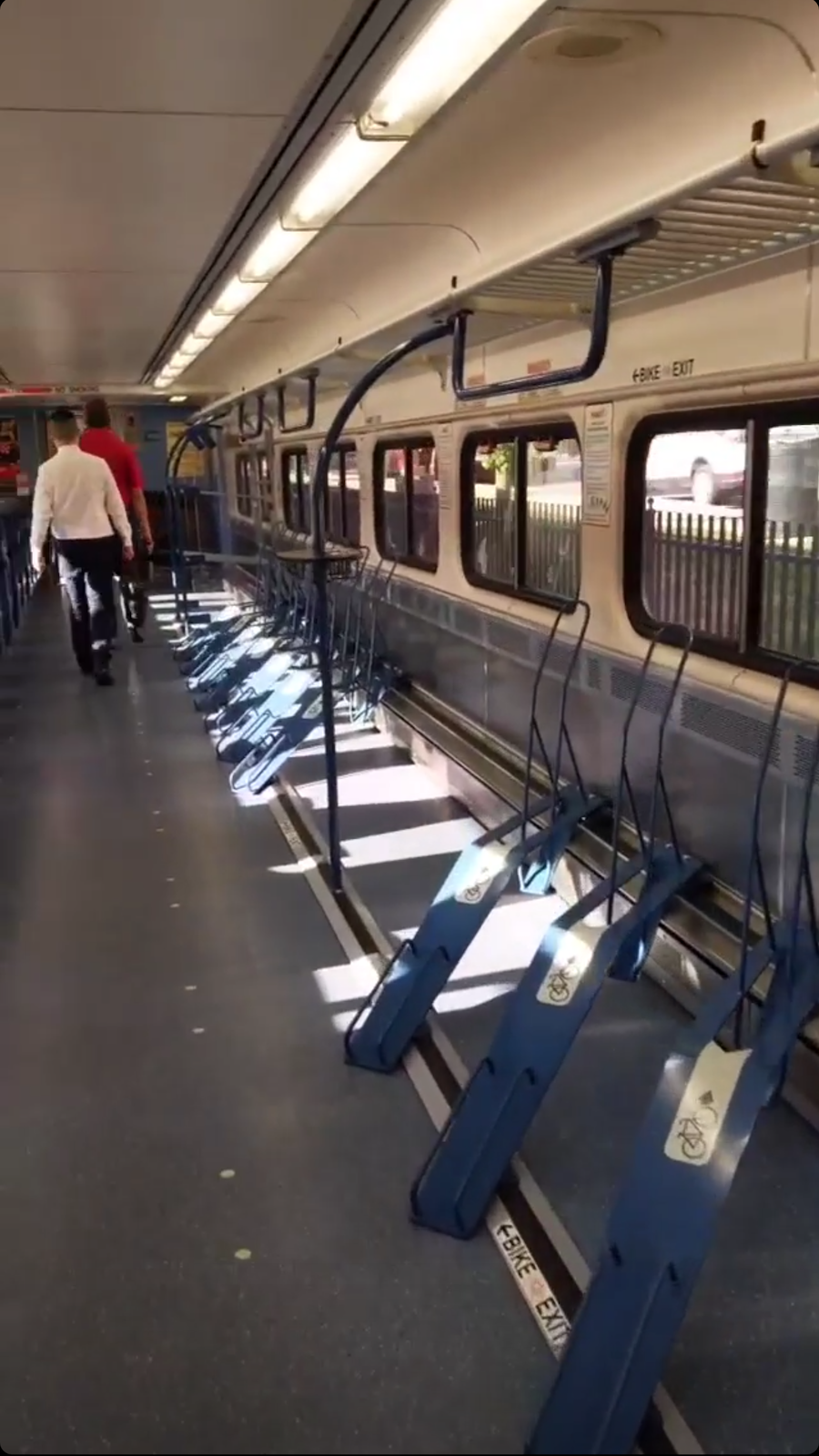
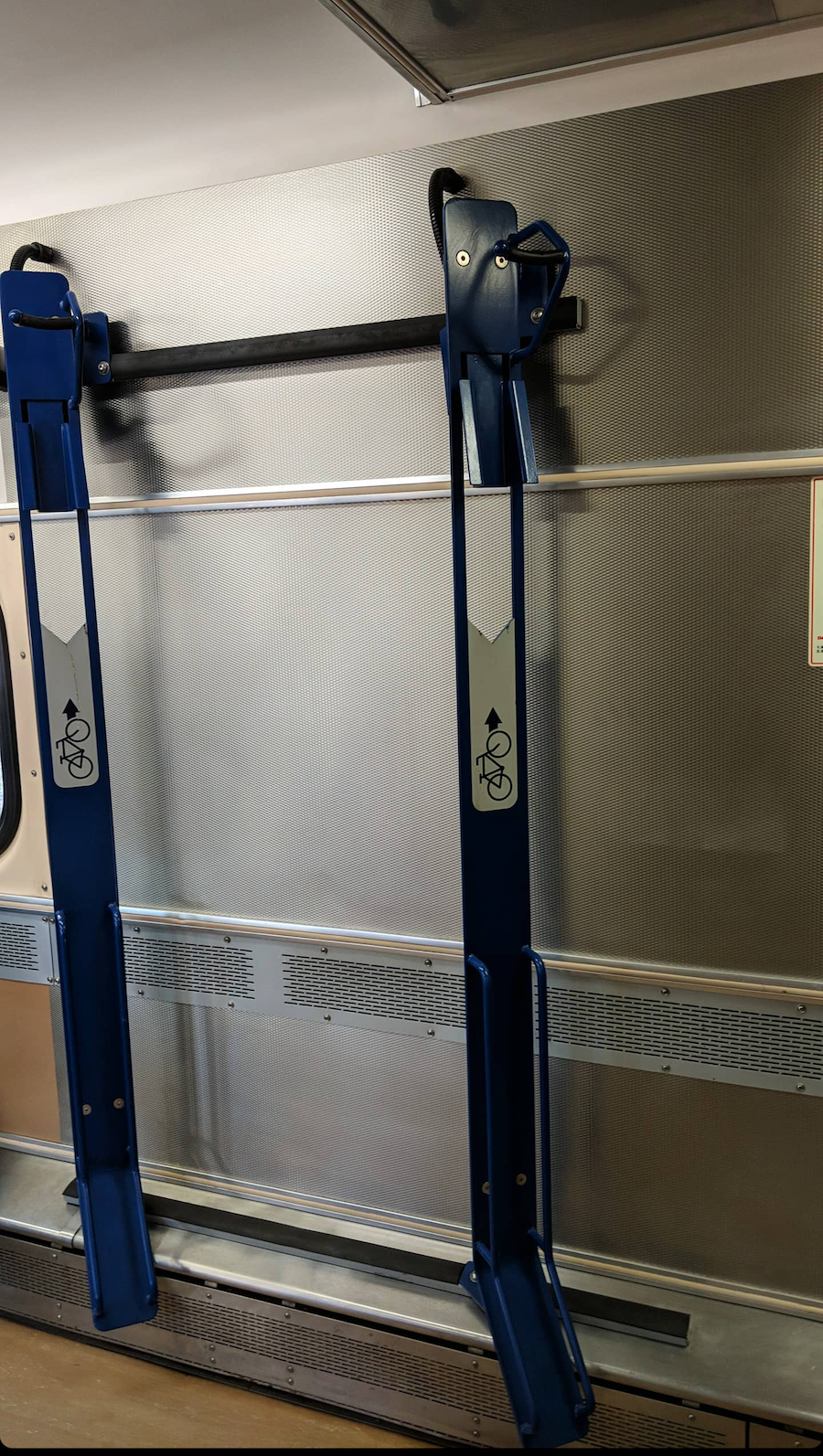
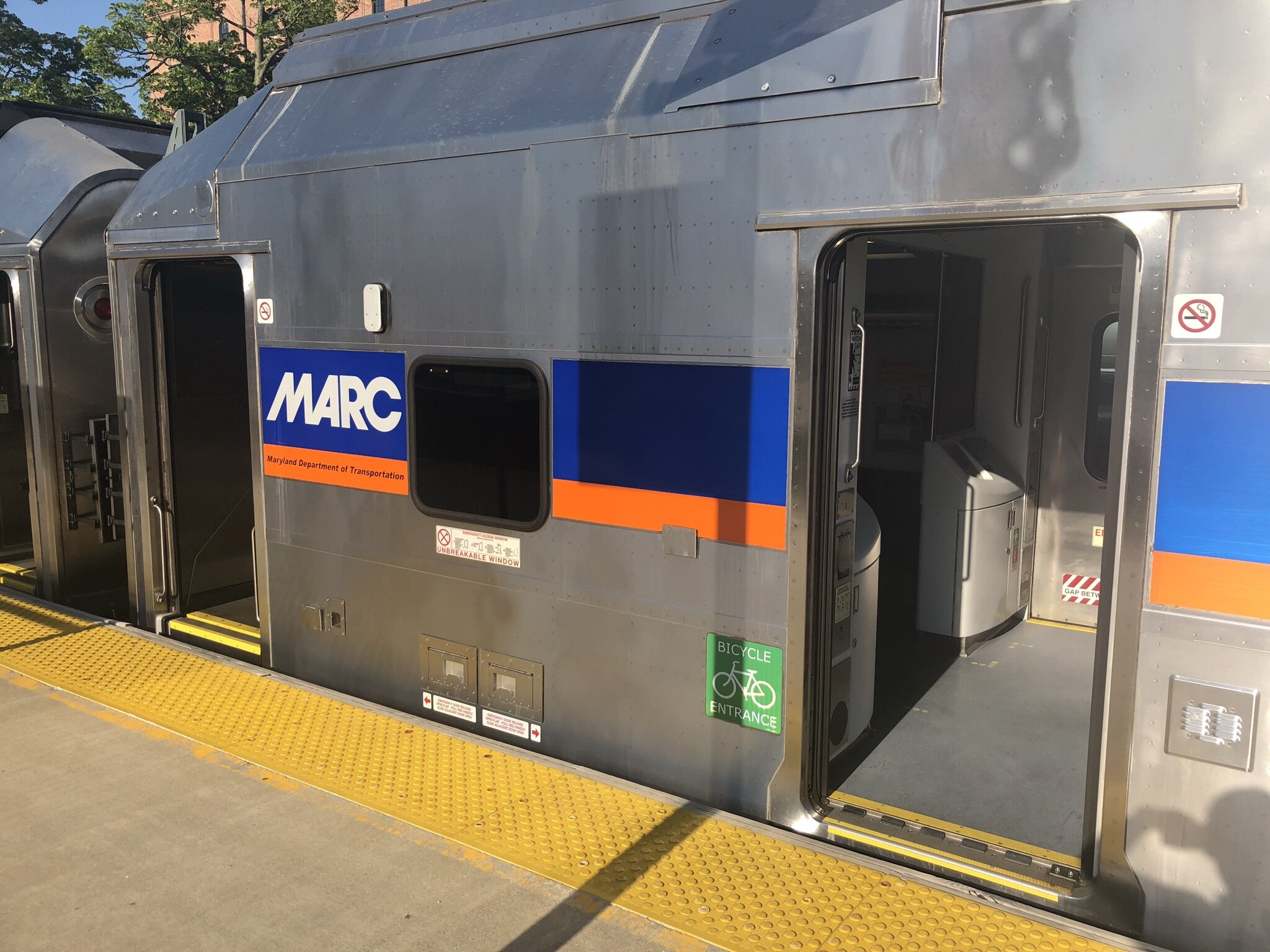
There are four different MARC car styles with bike parking. One type of car is a “bike car” and has 10+ horizontal parking spots. Two types of cars have 2 vertical spots at each end of the car with exterior green lights to signal space availability. And finally, one car where bikes can be secured over folding chairs with bungee cords. These are the same style of the seats that can be used for users with wheelchairs and other accessibility needs.
Each MARC train will have a variation of cars, and therefore a variation of bike parking. It’s likely that people will have multiple options for parking their bike on the train, not just folding chair spots.
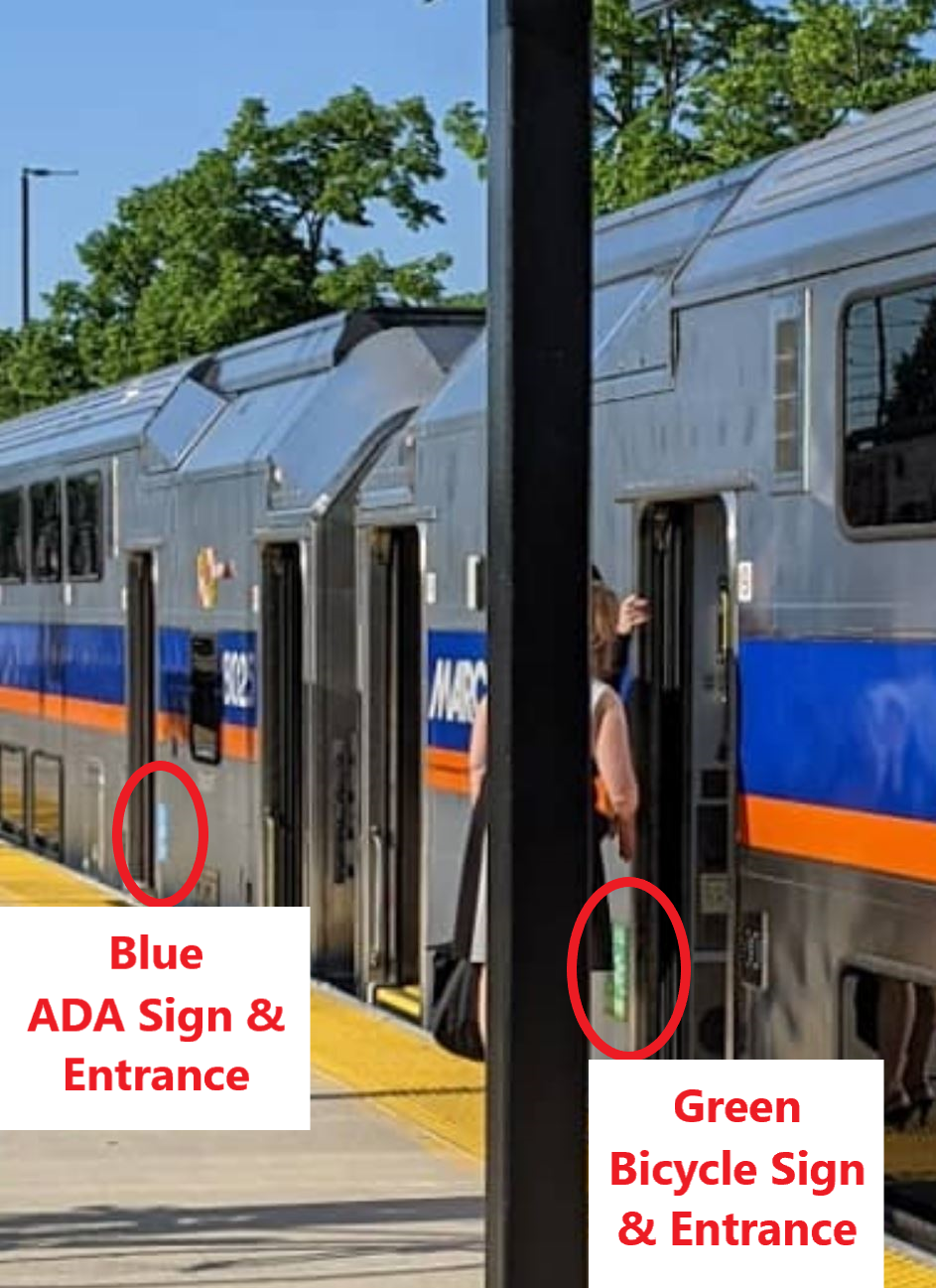
On cars with folding chairs, only one of the two entrances will be allowed for bike parking; cyclists should look for a green “Bicycle Entrance” sign adjacent to the car doors to know where to park their bike. The other end will have blue ADA signs to indicate the ADA entrance.
One side of these cars will always have dedicated ADA seating, and the MTA stated that people with disabilities will have priority over bicycles for all spots and people sitting in the folding seats on either end are not required to move for bicycles.
Obviously conflict between users could still arise and this has the potential to lead to harm. MTA is using the 90% decline in ridership to test the new policy. Ultimately as demand for the MARC increases, they must expand capacity for all types of users and prioritize ADA needs. The MTA should receive more funding for all of its services; including MARC trains, which could all have a dedicated bike parking car to increase accessibility and reduce conflicts.
MTA recently released a video that demonstrates how to park your bike on the various types of MARC train cars, available to watch here. For more details about using bikes with MTA services, visit MTA’s website.
We hope this helps answer some questions.